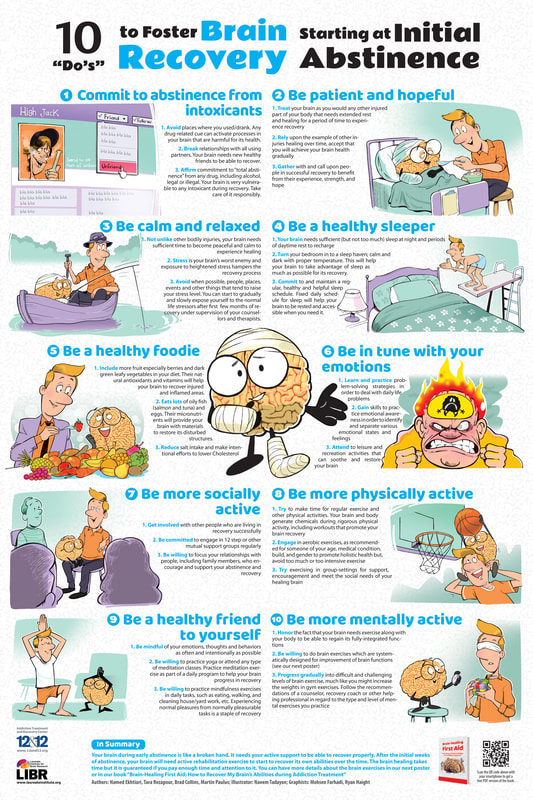
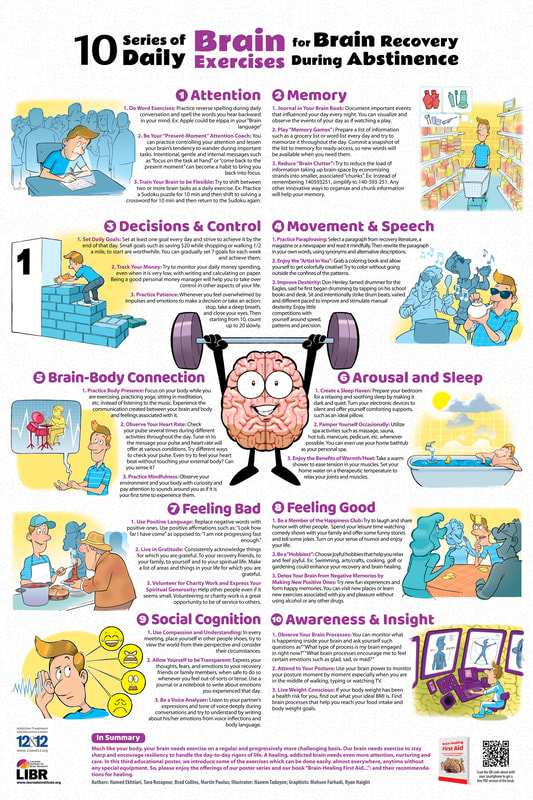
Brain Awareness for Addiction Recovery Initiative (BARI) works to help people who suffer from substance use disorders and their families have a better understanding about how brain is affected by drug addiction and how they can help the brain in the process of recovery. In a collaboration with Drs Martin Paulus, Robin Aupperle, and Tara Rezapour and Mr. Brad Collins, Dr. Hamed Ekhtiari developed a standalone, cartooned, neuroscience-informed psychoeducation (NIPE) package. NIPE incorporates neuroscience content, using the NIMH Research Domain Criteria (RDoC) as the basic framework. RDoC dimensions include negative valence (e.g., anxiety and loss), positive valence (e.g., reward), cognitive systems (e.g., attention, executive control, and working memory), social processes (e.g., affiliation), and arousal/modulatory systems (e.g., sleep–wake). NIPE uses cartoons and affiliated text to promote insight and metacognitive awareness and increase motivation for brain recovery. Some of the NIPE messages are organized in three posters in two different versions for male and female audience. NIPE posters are translated and culturally adopted by local scientific authorities in 22 languages in 5 continents so far. Addiction scientists and practitioners are welcome to send LIBR an email if they are interested to translate the posters in other languages.
NIPE materials are organized into a structured psychoeducation package for 4 sessions called “Brain Healing First Aid”. NIPE materials are also incorporated into a larger brain training/rehabilitation program for substance use disorders in 14 sessions (Neurocognitive Empowerment for Addiction Treatment (NEAT) or simply Brain Gym for Recovery).
BARI plans for other brain awareness activities/materials to promote brain recovery.
NIPE materials are organized into a structured psychoeducation package for 4 sessions called “Brain Healing First Aid”. NIPE materials are also incorporated into a larger brain training/rehabilitation program for substance use disorders in 14 sessions (Neurocognitive Empowerment for Addiction Treatment (NEAT) or simply Brain Gym for Recovery).
BARI plans for other brain awareness activities/materials to promote brain recovery.
BARI Posters Are Available in 22 Languages
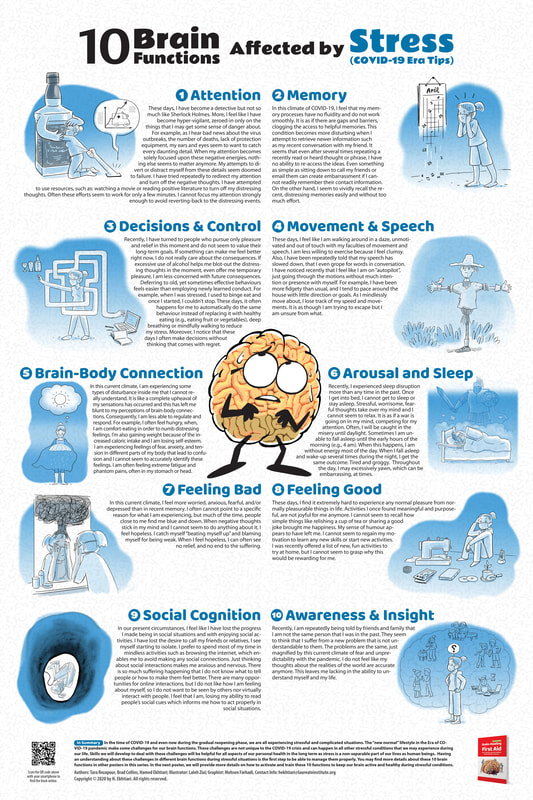
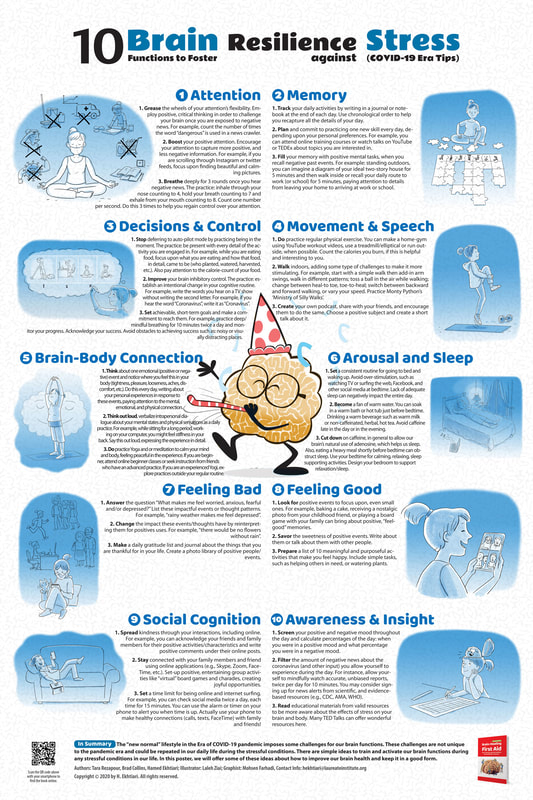
BARI Posters on Stress and Resilience During COVID-19
|
BARI COVID-19 Posters in English
COVID-19 Era Tips BARI COVID-19 Posters in French
|
Featured Videos
|
Introducing "Brain Healing First Aid" and "Brain Gym for Recovery" Programs, Innovations in Mental Health, Zarrow Meeting, October 2018
|
Brain Healing First Aid Workshop for Drug and Alcohol Counsellors, 12&12 Addiction Treatment Center, Tulsa, OK, November 2018
|
Brain Rehabilitation for Drug Addiction: Hopes and Challenges, Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP2019) meeting, Nelson, New Zealand, September 2019
|
|
Neurocognitive Education, Training and Rehabilitation for Addiction Treatment Workshop, PART ONE: Psychoeducation, Auckland New Zealand, September 2019
|
Neurocognitive Education, Training and Rehabilitation for Addiction Treatment Workshop, PART TWO: Rehabilitation, Auckland New Zealand, September 2019
|
BARI Introduction in International Society for Addiction Medicine (ISAM2019) meeting, New Delhi, November 2019
|
|
Basics of BARI, Catholic Charities of Eastern Oklahoma Psalm 127:1 Summit, January 2019, Tulsa, OK
|
Basic Concepts in Neurocognitive Rehabilitation for Drug Addiction, American Psychological Association (APA) Meeting, August 2019, Chicago
|
Drug Addiction Prevention from a Neuroscience Perspective, November 2019, The University of Tulsa
|
|
Workshop: Neuroscience Informed Psychoeducation (NIPE) for Drug Addiction, Session One
|
Workshop: Neuroscience Informed Psychoeducation (NIPE) for Drug Addiction, Session Two
|
Workshop: Neuroscience Informed Psychoeducation (NIPE) for Drug Addiction, Session Three
|
Featured Publications
Ongoing Trials
Neurocognitive Empowerment for Addiction Treatment (NEAT) in Opioid Use Disorder and Amphetamine Use Disorder
Funded by Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (OCAST)
PI: Hamed Ekhtiari, MD, PhD
Co-I: Robin Aupperle, PhD
The aim of this study is to characterize clinical efficacy for an intervention targeting neurocognitive deficits in opioid and/or methamphetamine addiction by enhancing awareness and use of neurocognitive skills in the context of substance use recovery. This aim will be accomplished by randomizing 80 subjects with opioid and/or methamphetamine use disorder who are already enrolled in substance use treatment in the state of Oklahoma to also complete the "Neurocognitive Empowerment for Addiction Treatment" (NEAT) program.
NEAT will be novel in (a) its use of cartoons, brain awareness games and real-life scenarios to ensure it is interactive and engaging, (b) the focus on the role of neurocognitive deficits in recovery from substance use and co-occurring mental health symptomatology, and (c) its incorporation of neuroscientific findings specific to substance use to the training and exercise strategies. Subjects will be followed up for twelve months after starting the program with different measures for addiction and mental health recovery to explore the efficacy of NEAT compared to the control intervention. Using LIBR's cutting-edge neuroimaging facilities before and after interventions, this study has the unique opportunity to monitor not only clinical outcomes, but also potential changes NEAT may have on brain structure and function. In case of finding reasonable clinical efficacy for NEAT, it will be hopefully integrated as a manualized brain rehabilitation program to the substance use treatment programs.
BARI team is happy to help other sites across the world to run similar trials with NEAT or NIPE packages in different treatment contexts.
Funded by Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (OCAST)
PI: Hamed Ekhtiari, MD, PhD
Co-I: Robin Aupperle, PhD
The aim of this study is to characterize clinical efficacy for an intervention targeting neurocognitive deficits in opioid and/or methamphetamine addiction by enhancing awareness and use of neurocognitive skills in the context of substance use recovery. This aim will be accomplished by randomizing 80 subjects with opioid and/or methamphetamine use disorder who are already enrolled in substance use treatment in the state of Oklahoma to also complete the "Neurocognitive Empowerment for Addiction Treatment" (NEAT) program.
NEAT will be novel in (a) its use of cartoons, brain awareness games and real-life scenarios to ensure it is interactive and engaging, (b) the focus on the role of neurocognitive deficits in recovery from substance use and co-occurring mental health symptomatology, and (c) its incorporation of neuroscientific findings specific to substance use to the training and exercise strategies. Subjects will be followed up for twelve months after starting the program with different measures for addiction and mental health recovery to explore the efficacy of NEAT compared to the control intervention. Using LIBR's cutting-edge neuroimaging facilities before and after interventions, this study has the unique opportunity to monitor not only clinical outcomes, but also potential changes NEAT may have on brain structure and function. In case of finding reasonable clinical efficacy for NEAT, it will be hopefully integrated as a manualized brain rehabilitation program to the substance use treatment programs.
BARI team is happy to help other sites across the world to run similar trials with NEAT or NIPE packages in different treatment contexts.
Featured Stories
|
South Korea: Tae-Yeon Hwang, MD, PhD, MPH, director of division of mental health service and planning at the national center for mental health (NCMH), Ministry of Health and Welfare, Seoul, Korea and president of Korean association of social and community psychiatry has supervised a group of drug addiction experts to translate and culturally adopt the BARI materials and Brain Healing First Aid in to Korean. BARI posters printed and distributed in 700 addiction treatment centers across South Korea during the International Society for Addiction Medicine (ISAM2018) meeting in Busan.
Israel: The Hebrew version of the posters was made by Dr. Dorit Porat and Dr. Ziv Carmel, both psychiatrists who also practice addiction medicine, and Ofra Bareket, an occupational therapist with extensive experience in psychiatry and cognitive behavioral therapy. The Hebrew version of the posters was presented during the annual "Addiction Academy" conference organized by the Israeli Society of Addiction Medicine on March, 2019 [Photo taken there]. The hard and soft copies of posters were distributed to therapists and treatment centers country wide and feedback was very positive from both therapists and patients. There is a significant interest in the posters among both addiction and general mental health professionals and the availability of translations to multiple languages is a big advantage due to the ethnic heterogeneity of the country's population.
Austria: Claudia I. Rupp, PhD, and David Junker, MSc, Department of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics of the Medical University Innsbruck, in Innsbruck, Austria, translated the BARI posters into German. In November 2019, they held a presentation at the DGPPN (German Association of Psychiatry, Psychotherapy and Neurology) congress 2019 in Berlin, Germany. They are working on the German version of the BARI Booklet “Brain Healing First Aid”, and plan to implement NIPE materials into the treatment of alcohol use disorder.
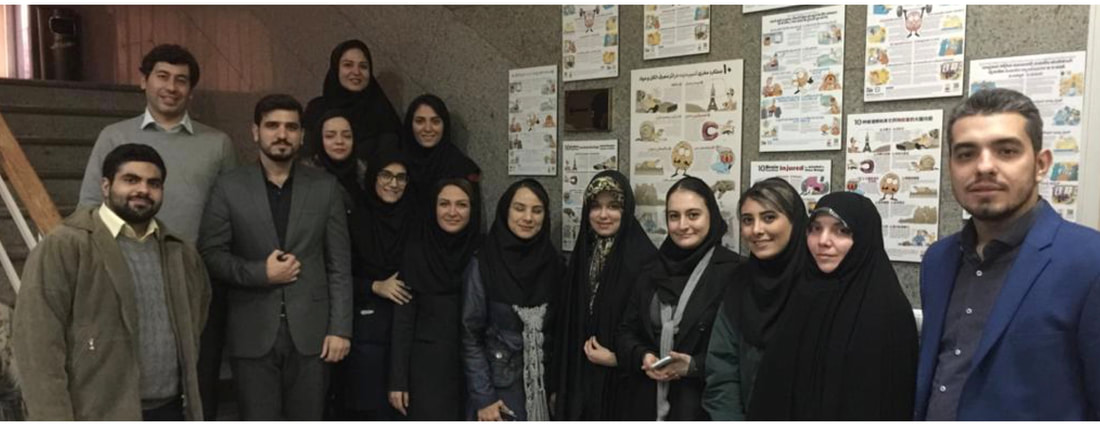
Iran: The Persian version of the BARI posters are being printed and distributed in 3000 addiction treatment centers across the country by Iranian National Center for Addiction Studies. A team of cognitive and clinical psychologists led by Dr Tara Rezapour (photo) are running a trial on the efficacy of BARI materials to increase metacognitive awareness, insight and motivation for recovery among people with methamphetamine and opioid use disorders in Tehran.
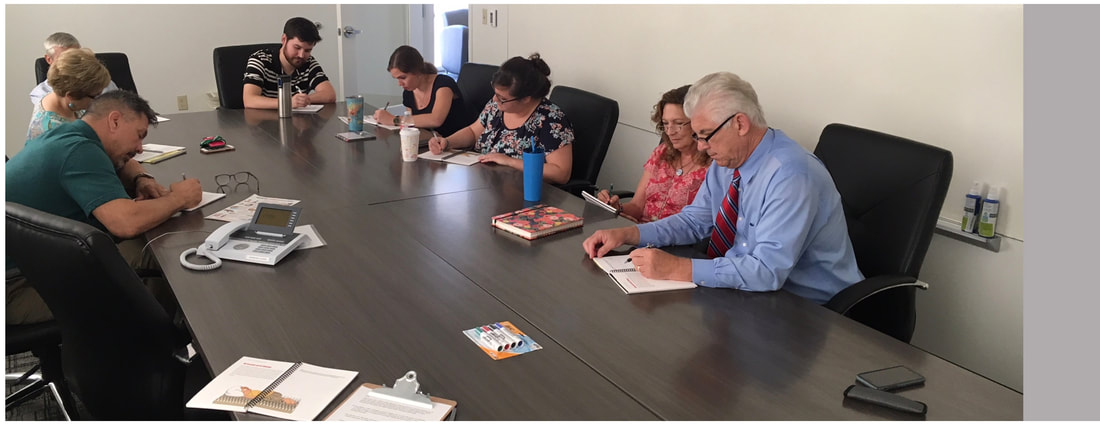
US, Richmond: In a half a day workshop at Virginia Common Wealth University (VCU) organized by Dr Jasmin Vassileva, we trained a group of therapists to run the Brain Healing First Aid as a 4 session neuroscience informed psychoeducation intervention for people in recovery. We are also developing a prevention-based intervention based on the BARI materials with Dr Vassileva.
|
Sweden: Mr Lars Gustafsson, Psychologist at Adult Psychiatry Unit, Kungsbacka, Region Halland in Sweden translated the BARI posters into Swedish. Lars did a presentation of BARI/NIPE November 28th, 2019 for 250 drug and alcohol professionals in Varberg, Halland. Lars is planning to run pilot studies with Brain Healing First Aid package in outpatient environments in Halland starting 2020. He has also been invited to present BARI/NIPE in other Swedish regions.
United Arab Emirates (UAE): Local organizing committee (UAE national rehabilitation center (NRC)) of the international society for addiction medicine annual meeting (ISAM2017) in Abu Dhabi provided a table for BARI during the meeting to present its work. Following the meeting, professor Mustafa al’Absi, Max & Mary La Due Pickworth endowed chair at the University of Minnesota Medical School and the chair of the Africa and Middle East congress on addiction (AMECA) and Dr Obada al’Zoubi, Laureate Institute for Brain Research, translated the BARI posters into Arabic.
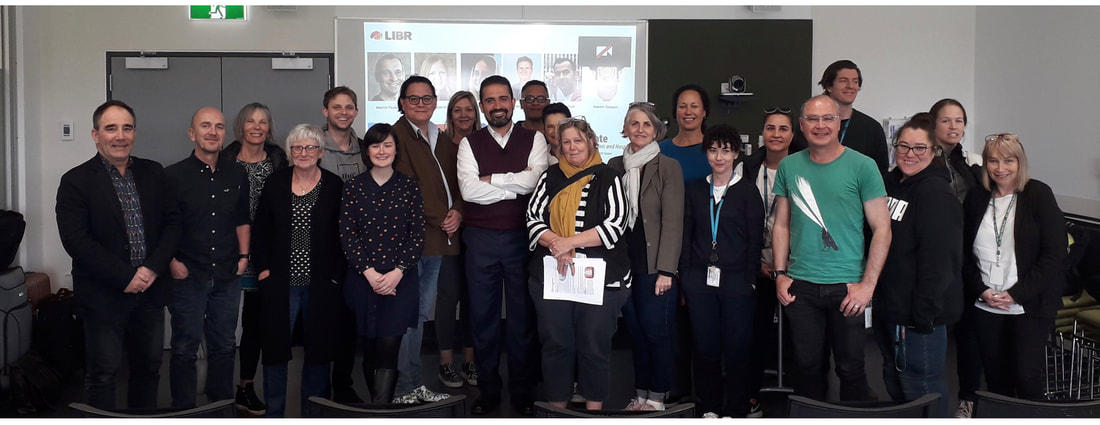
New Zealand: With an invitation from the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP), Dr Hamed Ekhtiari presented a keynote talk and a workshop at RANZCP2019 18-20 September in Nelson, NZ on brain awareness and cognitive rehabilitation for addiction treatment. On September 23rd, Matua Raki, the national center for addiction workforce development in New Zealand, held a full day workshop instructed by Hamed in Auckland for representatives from addiction treatment centers across New Zealand (photo) on cognitive training for addiction treatment.
US, Tulsa: In a pilot study, drug and alcohol counselors at the Laureate Psychiatric Clinic and Hospital (LPCH) led by Mr. Allan Gates are being trained in a 4 session continuing education course to use BARI materials as an integral part of their psychoeducation to people who are in the LPCH intensive outpatient program. They found BARI materials engaging and a great addition to their usual treatment. The BARI team will be happy to run similar ToT workshops for other addiction treatment centers. Recorded workshops are available in the BARI page as well.
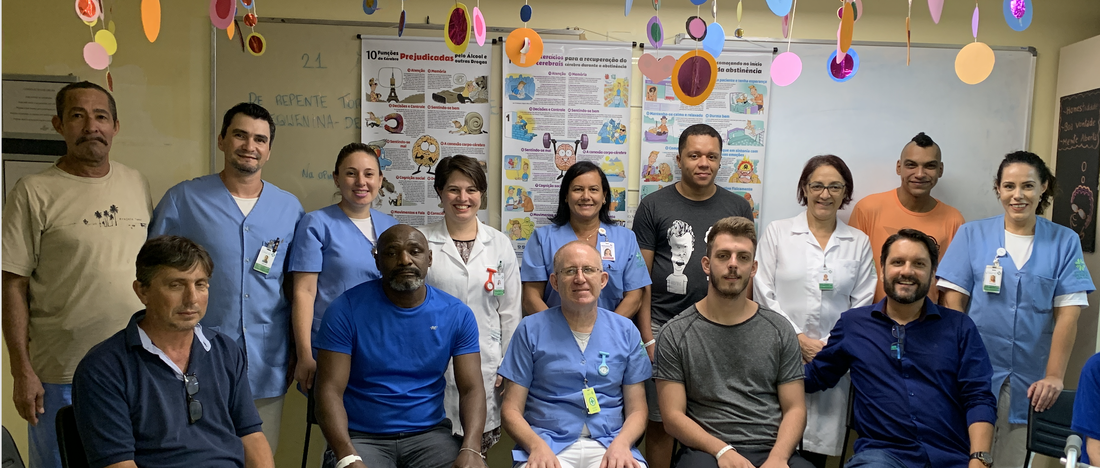
Brazil, Porto Alegre: Dr Felix Kessler, Psychiatrist and Professor, Department of Psychiatry and Legal Medicine, Graduate Program in Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences (PPG) at Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul (UFRGS) and President of the Centro de Estudos Luís Guedes (CELG) and his team translated the BARI posters into Portuguese and are using them as neuroscience-informed psychoeducation materials in the Hospital de Clinicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA).
|